告别选型焦虑!驱动器选对的核心逻辑(中英文)
选择驱动器,无论是用于新应用还是替换现有驱动器,都不必是一件令人头疼的事。成功的关键在于提出一系列合乎逻辑且经过深思熟虑的问题。
Selecting a drive, whether for a new application or to replace an existing one, doesn’t have to be a traumatic experience. The key to success lies in asking a logical sequence of thoughtful questions.
目标
Learning Objectives
• 了解驱动系统的核心部件和可选附件。
• 确定应用的关键机电需求。
• 确定应用的关键电子需求。
如果一台电动工业机器在运转,那么很可能是由驱动器(即电子控制的齿轮电机)来控制其运动的。虽然普通齿轮电机已经为工业发展服务了一个多世纪,但价格低廉的电子驱动器成为主流技术也只有几十年的时间。因此,工厂工程师和维护人员在选择驱动器时可能会感到不知所措。传统上,驱动器制造商会通过销售工程师来指导这一过程,但现在许多制造商都提供在线选择工具或智能手机应用程序作为替代方案。虽然这些工具无疑使选择过程更加便捷,但要正确使用它们却并非易事。
幸运的是,这个问题有一个简单的解决方案:在使用选择工具之前提出正确的问题。认真定义问题并整理应用需求,是顺利成功选择驱动器的关键。本文概述了在使用驱动器制造商的选型工具之前,自己应该了解的问题。
Recognize the core components and optional accessories making up a drive train.
Identify an application’s key electromechanical requirements.
Identify an application’s key electronics requirements.
If an electrically powered industrial machine moves, chances are that a drive—an electronically controlled gearmotor—orchestrates that motion. While ordinary gearmotors have moved industry for over a century, inexpensive electronic drives have been mainstream technology for just a few decades. Consequently, plant engineers and maintenance personnel may feel uncomfortable about selecting a drive. Traditionally, drive manufacturers guided this process through their sales engineers, but many now offer online selection tools or smartphone apps as an alternative. While these certainly make the selection process more convenient, they can be daunting to use correctly.
Happily, there’s a simple solution to this problem: ask the right questions before sitting down to the selection tool. Thoughtfully defining the problem and organizing the application’s requirements paves the way to a smooth and successful selection experience. This article outlines the questions you should ask yourself as you prepare to use a drive manufacturer’s selection tool.
驱动系统
The Drive Train
驱动系统包含为应用提供动力的所有部件,包括驱动器本身。驱动器(图 1)由三个核心部件组成:齿轮箱、电动机和变频器 (VFD)。它可以直接连接到应用,也可以通过其他传动元件(例如皮带、链条或主轴)传递动力。无论哪种方式,驱动器都必须配备合适的联轴器和安装装置。这些装置包括柔性联轴器、法兰、底座或扭矩臂。
The drive train contains everything that powers the application, including the drive itself. The drive (Figure 1) has three core components: a gearbox, an electric motor, and a variable frequency drive (VFD). It may connect directly to the application, or it may deliver power through additional transmission elements, such as a belt, chain, or spindle. In either case, the drive must have appropriate coupling and mounting devices. These include flexible couplings, flanges, feet, or torque arms.
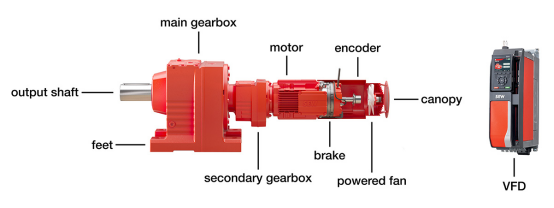
图 1:驱动器及其部分可选配件。图片由 SEW-EURODRIVE 提供。
Figure 1: A drive and some of its optional accessories. Courtesy SEW-EURODRIVE
电机可能需要制动器,用于停止负载或将其固定到位。如果应用需要精确的速度控制或定位,则需要电机编码器。当应用由 PLC 或其他工业控制器管理时,变频器可能需要合适的现场总线接口或一些额外的输入输出。
用户提出的问题将定义驱动器。这些问题将阐明主要组件并找出所需的专用附件。这些问题大致将驱动器分为机电组件和电子组件。
The motor may require a brake, either to stop the load or hold it in place. If the application requires precise speed control or accurate positioning, a motor encoder will be necessary. When a PLC or other industrial controller manages the application, the VFD will probably need a suitable fieldbus interface or some extra inputs and outputs.
The questions you’ll be asking define the drive. They flesh out the main components and tease out the specialized accessories required. The questions broadly divide the drive into its electromechanical and electronic components.
核心机电问题
Core Electromechanical Questions
首先要确定应用的运动方式。是旋转运动还是直线运动?如果是直线运动,是水平运动、垂直运动还是倾斜运动?垂直和倾斜运动通常需要制动器,而水平运动则可能需要也可能不需要。务必确定运动的占空比。连续运行的应用,例如简单的传送带或鼓风机,可以使用普通的交流感应电机。而执行重复序列的循环应用,例如包装机,则可能需要动力更强的永磁同步电机。
在考虑应用的运动方式时,还要确定预期负载。除了负载的大小之外,还要确定负载主要是静态的还是动态的。对于负载相对静态的应用,选择合适的驱动器比较简单。如果负载变化范围很大或可能突然变化,则驱动器需要更大的服务系数。此外,务必确定应用的加速度要求。在循环应用中,电机必须提供足够的扭矩,才能在规定的时间内加速负载。永磁同步电机比普通感应电机更能承受剧烈的加速。
确定应用所需的转速、扭矩和功率。这些参数有助于选择合适的电机和齿轮箱。转速和扭矩要求也决定了合适的齿轮箱传动比。务必明确驱动装置与应用的连接方式。列出相关细节,例如轴径、法兰和底座要求以及联轴器类型。最后,如果应用需要制动器,请确定所需的制动扭矩。
近年来,由于能源成本不断上涨以及法规强制要求使用高效电机,应用效率变得越来越重要。之前回答的问题可能会引导选型工具选择特定的电机效率等级。例如,连续运行应用需要高效(IE3)电机。可以通过指定齿轮箱类型和安装位置来进一步提高效率。基于螺旋齿轮或锥齿轮的齿轮箱通常比蜗轮蜗杆齿轮箱效率更高,因此在效率至关重要的情况下,它们是更佳的选择。
同样,变速箱的安装位置也会影响效率,因为位置决定了壳体内需要多少润滑油才能润滑各级齿轮。垂直安装位置通常需要更多的润滑油,这会导致齿轮在润滑油中搅动时产生更大的搅动损失。因此,应尽可能选择所需润滑油量最少的安装位置。每个制造商都有自己的安装位置标识方案(图 2)。务必理解该方案,以便正确指定变速箱的安装位置。
Begin by identifying the application’s motion. Is it rotary or linear? With linear motion, is it horizontal, vertical, or angled? Vertical and angled applications usually require a brake, while horizontal ones may or may not. Be sure to identify the motion’s duty cycle too. Continuous duty applications, like simple conveyors or a blower, can work well with an ordinary AC induction motor. Cyclic applications performing repetitive sequences, such as packaging machines, may benefit from a more dynamic permanent magnet synchronous motor.
While you’re thinking about the application’s motion, identify the expected loads. Besides their magnitude, also determine whether they’re predominantly static or dynamic. Sizing a drive for an application with relatively static loads is simple. If the load varies widely or can change abruptly, the drive will need a larger service factor. Be sure to identify the application’s acceleration requirements too. In cycling applications, the motor must deliver sufficient torque to accelerate the load within the time constraints. PM synchronous motors can handle aggressive acceleration better than ordinary induction motors.
Determine the application’s speed, torque, and horsepower requirements. These help size the motor and gearbox. The speed and torque requirements also determine the appropriate gearbox ratio. Be sure to identify how the drive will connect to the application. List appropriate details like shaft diameter, flange and feet requirements, and coupling type. Finally, if the application needs a brake, identify the required braking torque.
Application efficiency has progressively become more important in recent years due to rising energy costs and legislation mandating efficient motors. Questions that you’ve already answered may steer the selection tool towards a particular motor efficiency rating. For example, a continuous duty application requires a premium efficiency (IE3) motor. You can improve efficiency even further by requesting a particular gearbox style and mounting position. Gearboxes based on helical or bevel gears tend to be much more efficient than those containing worm gears, so they’re preferable when efficiency is paramount.
Similarly, the gearbox mounting position influences efficiency since position determines how much oil the housing must contain to keep the gear stages lubricated. Vertical mounting positions often require more lubricant, which leads to higher churning losses as the gears plow through the oil. Whenever possible, select a mounting position that requires the least lubricant. Every manufacturer has its own mounting position identification scheme (Figure 2). Be sure that you understand it, so you can correctly specify the gearbox mounting position.

图 2:不同制造商的变速箱安装位置标识各不相同。这是 SEW-EURODRIVE 的系统。图片由 SEW-EURODRIVE 提供。
Figure 2: Gearbox mounting position identifiers vary among manufacturers. This is SEW-EURODRIVE’s system. Courtesy SEW-EURODRIVE
环境机电问题
Environmental Electromechanical Questions
已经解决了最棘手的机电问题。剩下的问题有助于确定确保驱动器与应用完美匹配所需的其他因素。首先,请描述应用的运行环境。是在室内还是室外?环境干净还是脏?潮湿还是干燥?是否存在腐蚀性化学品?驱动器是否需要定期清洗?
这些问题的答案将决定驱动器的材料、保护涂层、密封件和电缆。例如,在禽肉加工厂运行的驱动器每天需要用热水和腐蚀性清洁剂多次清洗。普通的保护涂层无法在这种条件下长期使用。采用灌封电机绕组和导管盒连接的不锈钢驱动器是更好的选择。
另一方面,环境可能干燥但仍然非常恶劣。驱动矿石或岩石破碎机的驱动器必须承受大量的粉尘和磨蚀性颗粒。这些可能需要多个轴封,或者使用专门设计的轴封来防止磨蚀性颗粒进入。驱动装置可能还需要轴承润滑装置,以便更轻松地进行定期润滑脂更换。
确定应用的预期温度范围。环境温度是否异常高或低?温度会影响润滑油的选择。矿物油和润滑脂在日常温度下性能良好,而专用合成润滑油则更适合极端高温和低温环境。变速箱和电机在寒冷环境下可能需要辅助加热,而在炎热环境下则需要更强劲的冷却。在考虑润滑油时,请记住食品加工和制药机械通常需要食品级润滑油。
You’re past the most difficult electromechanical questions. Those that remain help identify additional factors needed to ensure a good match between the drive and the application. Begin by describing the application’s operating environment. Is it indoors or outdoors? Clean or dirty? Wet or dry? Are there harsh or corrosive chemicals involved? Will the drive require regular wash-down?
The answers to these questions determine the drive’s materials, protective coatings, seals, and cabling. A drive operating in a poultry processing plant, for example, requires multiple wash-downs per day with hot water and caustic cleaning agents. Ordinary protective coatings won’t survive these conditions for very long. A stainless steel drive with potted motor windings and conduit box connections is a much better choice.
On the other hand, the environment can be dry but still very harsh. Drives powering ore or rock crushing machines must endure heavy dust and abrasive grit. These will probably require multiple shaft seals or ones specifically designed to keep abrasives out. The drive may also need bearing re-lubrication fittings to make regular grease changes simpler.
Identify the application’s expected temperature range. Is it unusually hot or cold? Temperature affects lubricant choices. Mineral oils and greases perform well at everyday temperatures, whereas specialized synthetics are better choices for hot and cold extremes. The gearbox and motor may require auxiliary heat in a cold environment or more aggressive cooling in a hot one. While you’re thinking about lubricants, remember that food processing and pharmaceutical machines often need food-grade lubricants.
核心电子元件问题
Core Electronics Questions
至此,已提出足够多的问题来确定电机和齿轮箱。剩余的问题将帮助选择变频器 (VFD) 及其附件。如果之前没有使用过变频器,这些问题可能比较陌生。虽然所有变频器的功能大同小异——控制电机——但它们在功能和预期应用方面却大相径庭。再次强调,提出正确的问题将有助于确定哪一款变频器最适合。
已经回答了一个同样重要的机电问题——应用所需的功率。此外,还要确定可用的电源电压和相数(单相或三相)。这些信息将决定变频器的规格并确定可能的型号。在大多数情况下,驱动器制造商会提供几种变频器来满足应用的基本电气要求。列出其他应用要求将有助于从中选择合适的型号。
首先确定应用的运行模式——是基于速度、位置还是扭矩。基于速度的应用最为简单,几乎任何变频器都能胜任。但务必确定所需的精度。入门级变频器可以处理精度要求不高的应用,例如风扇、水泵和鼓风机。需要更高精度的应用必须使用支持通过电机编码器进行闭环控制的变频器。虽然许多变频器可以运行在闭环模式下,但并非所有变频器都内置编码器接口。没有内置编码器接口的变频器需要额外购买接口板。该接口板必须与电机编码器的通信标准相匹配。
定位应用本质上需要更高级的变频器。它必须以特定速度运行电机,同时监控一个或多个编码器以确定应用的位置。到达指定位置后,它必须干净利落地停止电机。如果应用需要定位,请确定其定位类型(线性或角度)和所需的精度。这些信息也会影响编码器的选择。精确定位需要昂贵的高分辨率编码器,而基本定位则可以使用更经济的选择。
需要基于扭矩控制的应用并不常见,因此并非所有变频器都支持这种模式。这类应用要求变频器通过调节驱动扭矩来维持负载上的特定张力。例如,绕线机和卷筒纸印刷机的送纸系统都属于此类应用。在每种情况下,变频器都会使用传感器(例如张力计)来监测导线或纸张上的张力。变频器利用这种反馈来生成维持目标张力所需的扭矩。如果应用是基于扭矩的控制,请确保变频器支持这种模式,并且能够与所需的传感器连接。
最后一个核心电子元件问题是:变频器(VFD)将如何集成到应用中。许多变频器制造商提供两种类型的产品:控制柜式和分散式(图 3)。顾名思义,控制柜式变频器安装在电子柜中。电线进出电子柜,将电源、电机和所有传感器连接到变频器。电子柜可以保护变频器免受环境影响,这在恶劣环境下运行尤为重要。
At this point, you’ve asked enough questions to specify the motor and gearbox. The remaining questions help select the VFD and its accessories. These may be unfamiliar territory if you’ve not worked with VFDs before. While all VFDs do much the same thing—control the motor—they vary widely in their features and intended applications. Again, asking the right questions will help you decide which one is right for you.
You’ve already answered an electromechanical question that is equally important for selecting the VFD—the application’s horsepower requirement. Additionally, determine the available power supply voltage and phase (single- or three-phase). These answers size the VFD and identify possible models. In most cases, a drive manufacturer will offer several VFDs that will satisfy your application’s basic electrical requirements. Listing additional application requirements will help you choose from among these.
Begin by identifying the application’s operating mode—whether it’s speed-, position-, or torque-based. Speed-based applications are the simplest, so almost any VFD can handle them capably. Do determine the accuracy required, however. Entry-level VFDs can handle applications with modest requirements—fans, pumps, and blowers, for example. Applications requiring higher accuracy must use a VFD that supports closed-loop control via a motor encoder. While many VFDs can operate in closed-loop mode, not all come with built-in encoder interfaces. Those that don’t will require an add-on interface board. This must match the motor encoder’s communications standard.
By their very nature, positioning applications require a more advanced VFD. It must run the motor at a specific speed while monitoring one or more encoders to determine the application’s position. Upon reaching the specified position, it must stop the motor cleanly and accurately. If your application requires positioning, determine its type (linear or angular) and the required accuracy. These answers will also influence the encoder selection. Precise positioning will require an expensive, high-resolution encoder, while basic positioning can get by with a more economical choice.
Applications requiring torque-based control are the least common, so not all VFDs support this mode. They require the VFD to maintain a specific tension on the load by adjusting the driving torque. A wire winder is an example, as is the paper feed system in a web printing press. In each case, the VFD monitors the tension on the wire or paper with a sensor, such as a dancer potentiometer. The VFD uses this feedback to generate the torque required to maintain the target tension. If your application is torque-based, be sure the VFD supports this mode and can interface with the required sensors.
For the final core electronics question, determine how the VFD will integrate into the application. Many VFD manufacturers offer their products in two styles: control cabinet and decentralized (Figure 3). A control cabinet VFD, as its name implies, lives in an electronics cabinet. Wires enter and exit the cabinet, connecting power, the motor, and any sensors to the VFD. The cabinet protects the VFD from the environment, especially important when operating under harsh conditions.

图 3:控制柜式(左)和分散式(右)变频器执行相同的任务,但方式截然不同。图片由 SEW-EURODRIVE 提供。
Figure 3: Control cabinet (left) and decentralized (right) VFDs perform the same task but in completely different ways. Courtesy SEW-EURODRIVE
分散式变频器采用不同的控制方式。它们直接安装在电机上或紧邻电机的位置。由于直接暴露于应用环境,分散式变频器通常具有较高的防护等级(IP),例如 IP66 或更高。分散式变频器能够更无缝地集成到应用中,并且由于其安装位置靠近电机,通常所需的布线也更少。分散式变频器在许多行业中正变得越来越受欢迎。一些驱动器制造商甚至提供“电子齿轮电机”——将齿轮箱、电机和变频器集成在一起(图 4)。这些产品为许多驱动难题提供了一种特别巧妙的解决方案。此外,一些产品效率极高,因为它们将超高效(IE4)电机与高效齿轮箱和变频器相结合。
Decentralized VFDs approach control differently. They mount either on the motor itself or very close to it. Since they’re exposed to the application’s operating environment, decentralized VFDs usually have relatively high IP (ingress protection) ratings, such as IP66 or higher. A decentralized VFD integrates more seamlessly into the application and typically requires less wiring since it mounts very close to the motor. Decentralized VFDs are becoming increasingly popular in many industries. Some drive manufacturers even offer “electronic gearmotors”—an all-in-one gearbox, motor, and VFD (Figure 4). These offer an especially elegant solution to many drive challenges. As a bonus, some are exceptionally efficient because they combine a super premium efficiency (IE4) motor with an efficient gearbox and VFD.

图 4:一款高效电子齿轮电机,集成了电机、螺旋锥齿轮箱和变频器。图片由 SEW-EURODRIVE 提供。
Figure 4: A highly efficient electronic gearmotor integrating a motor, a helical-bevel gearbox, and a VFD. Courtesy SEW-EURODRIVE
次级电子元件问题
Secondary Electronics Questions
确定核心电子元件需求后,提出一些问题,以了解影响变频器 (VFD) 的特殊功能。例如,许多应用都包含变频器必须监控的控制器或传感器。这些可能是拨动开关、按钮、限位开关或参考凸轮等数字设备,也可能是温度传感器、速度控制电位器或代表过程变量的电压等模拟设备。大多数变频器至少包含一些数字输入和输出,但并非所有变频器都支持模拟信号。在某些情况下,变频器可能需要扩展卡来增强其内置的 I/O。
最后,考虑应用将使用哪种控制方法来管理变频器。像风扇和水泵这样的简单应用可能依赖于变频器的前面板进行控制和状态显示。更复杂的应用可能通过开关、电位器和数字指示器以终端控制(二进制)模式操作变频器。
最复杂的应用使用 PLC 或类似的工业控制器来管理变频器。这些设备通常通过现场总线(一种强大的工业网络)与变频器 (VFD) 通信。现场总线控制提供了最大的灵活性和精细度,但也增加了复杂性。如果应用需要现场总线控制,则需要确定控制器品牌和型号,以及它使用的现场总线标准。较新的控制器使用基于以太网的现场总线,例如 EtherNet/IP™、Modbus® TCP 或 PROFINET®。较旧的控制器使用传统标准,例如 PROFIBUS® 或 DeviceNet™。大多数变频器制造商都支持多种现场总线标准。变频器可能内置现场总线接口,也可能需要添加扩展卡。
Once you’ve identified the core electronics requirements, ask questions that will reveal special features affecting the VFD. For example, many applications include controls or sensors that the VFD must monitor. These may be digital devices like toggle switches, pushbuttons, limit switches or a referencing cam. Alternatively, they may be analog devices, like temperature sensors, a speed-control potentiometer, or a voltage that represents a process variable. Most VFDs include at least a few digital inputs and outputs, but not all support analog signals. In some cases, the VFD may require an expansion card to augment its built-in I/O.
Finally, consider the control method that the application will use to manage the VFD. Simple applications like fans and pumps may rely on the VFD’s front panel for control and status display. More-sophisticated applications might operate the VFD in terminal control (binary) mode via switches, a potentiometer, and digital indicators.
The most sophisticated applications use a PLC or similar industrial controller to manage the VFD. These usually communicate with the VFD over a fieldbus—a robust industrial network. Fieldbus control provides maximum flexibility and sophistication but adds an extra layer of complexity. If the application requires fieldbus control, you’ll need to identify the controller brand and model, as well as the fieldbus standard it uses. Newer controllers use Ethernet-based fieldbuses such as EtherNet/IP™, Modbus® TCP, or PROFINET®. Older controllers use legacy standards such as PROFIBUS® or DeviceNet™. Most VFD manufacturers support multiple fieldbus standards. The VFD may have a built-in fieldbus interface or may require an add-in card.
选择驱动器
Selecting the Drive
至此,已收集齐使用驱动器制造商选型工具所需的一切信息。启用该工具,并回答其提出的问题,提供已收集到的信息。提前做好规划能让用户在选型过程中信心倍增,工具生成推荐结果后,也会更加安心。
At this point, you’ve gathered everything necessary to use the drive manufacturer’s selection tool. Fire it up and answer its questions, supplying the information that you’ve gathered. You’ll discover that thinking things through in advance will give you confidence as you work your way through the selection process, as well as afterwards when the tool generates its recommendations.
声明:
-文章转载自SEW,由爱泽工业翻译,如有侵权,请联系删除!
-如有偏颇,欢迎指正!

 沪公网安备31011002006738号
沪公网安备31011002006738号

