您的编码器在“说”哪种语言?详解工业通信协议(中英文)
绝对式编码器可以通过并行或串行线路、现场总线或基于以太网的协议(例如 EtherCAT)与控制器通信。在这些选项中,串行通信比并行线路(每个输出位都需要一对双绞线)更简单,非常适合那些复杂度不足以使用现场总线或基于以太网的协议的应用。
Absolute encoders can communicate with controllers through parallel or serial wiring, over a fieldbus, or via an Ethernet-based protocol such as EtherCAT. Of these options, serial communication is a simpler solution than parallel wiring (which requires a twisted pair of wires for each bit of output) and is well-suited for applications that aren’t complex enough to justify a fieldbus or Ethernet-based protocol.
SSI:同步串行接口
SSI: Synchronous Serial Interface

顾名思义,SSI 是一种同步协议,这意味着数据通过控制器提供的时钟信号(或脉冲)从编码器同步传输到控制器。编码器输出可以是二进制或格雷码,每个时钟脉冲传输一位数据,单圈编码器的标准字长为 13 位,多圈编码器的标准字长为 25 位。
As its name suggests, SSI is a synchronous protocol, meaning that data is transferred from the encoder to the controller synchronously via a clock signal, or pulse, provided by the controller. The encoder output can be in binary or gray code, and one bit is transmitted per clock pulse, with standard word lengths of 13 bits for single-turn encoders and 25 bits for multi-turn encoders.
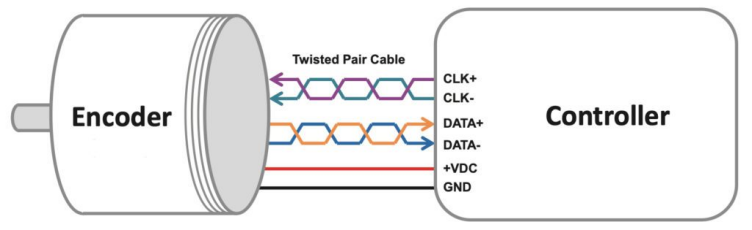
SSI编码器接口非常简单,仅需四根通信线(一对双绞线用于数据传输,一对双绞线用于时钟信号传输)和两根电源线。
图片来源:AccuCoder
The SSI encoder interface is simple, with just four wires for communication (a twisted pair for data and a twisted pair for clock signals) and two wires for power.
Image credit: AccuCoder
同步串行接口 (SSI) 使用两对双绞线进行通信,符合 RS-422 标准——一对用于传输差分数据信号,另一对用于传输差分时钟信号。此外,还有两根线用于为编码器供电。时钟频率(或数据传输速率)最高可达 1.5 MHz,具体取决于电缆长度。为了确保数据完整性,一些 SSI 编码器支持多次传输(也称为“多路径”或“环移”传输),即多次发送相同的数据,控制器会比较这些传输以确保它们匹配。
Synchronous Serial Interface uses two pairs of twisted wires for communication, per the RS-422 standard — one pair for differential data signals and one pair for differential clock signals. There are also two wires for power to the encoder. The clock frequency, or rate of data transmission, can be up to 1.5 MHz, depending on the length of the cable. To ensure data integrity, some SSI encoders support multiple transmission (also known as “multi-path” or “ringshift” transmission), in which the same data is sent multiple times and the controller compares the transmissions to ensure they match.
BiSS:双向同步串行接口
BiSS: Bidirectional Synchronous Serial Interface

双向同步串行接口(BiSS)是一种开放协议,与SSI类似,数据传输均由控制器发出的时钟信号同步。但BiSS的时钟频率最高可达10 MHz。BiSS也使用两对双绞线——一对用于传输数据信号,一对用于传输时钟信号——以及两根电源线。
与仅支持单向通信的SSI不同,BiSS支持双向通信,这意味着控制器可以读取和写入编码器中的非易失性存储器,其中的寄存器包含编码器标识信息。BiSS编码器还可以按需向控制器发送数据,例如温度。BiSS相对于SSI的另一个独特之处在于,在每个数据周期内,主设备会确定并补偿任何传输延迟,从而实现高达10 Mbps的数据传输速率。
BiSS的最新版本是BiSS-C(C代表连续),但该接口通常简称为“BiSS”。
The Bidirectional Synchronous Serial Interface is an open protocol and is similar to SSI in that data transmission is synchronized by clock signals from the controller, but with BiSS, clock speeds up to 10 MHz are possible. BiSS also uses two twisted pairs of wires — one pair for data signals and one pair for clock signals — plus two wires for power.
Unlike SSI, which only supports unidirectional communication, BiSS supports bidirectional communication, meaning the controller can read from and write to non-volatile memory in the encoder, where registers contain encoder identification information. BiSS encoders can also send data, such as temperature, to the controller on demand. Another unique feature of BiSS versus SSI is that within each data cycle, the master determines and compensates for any transmission delay, allowing data transmission rates up to 10 Mbps.
The most current version of BiSS is BiSS-C (C = Continuously), although the interface is typically referred to as simply “BiSS.”
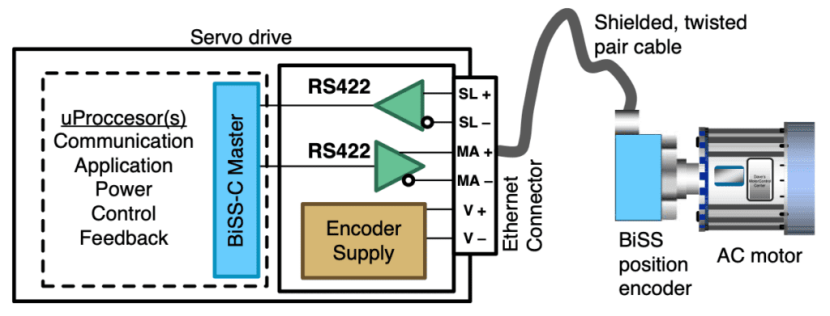
BiSS支持双向通信,因此使用两根线(MA+和MA-)用于控制器通信,两根线(SL+和SL-)用于编码器通信,此外还有两根线用于供电。
图片来源:德州仪器
BiSS allows bidirectional communication, and so uses two wires for communication from the controller (MA+ and MA-) and two wires for communication from the encoder (SL+ and SL-), plus two wires for power.
Image credit: Texas Instruments
与SSI编码器不同,BiSS编码器可以点对点连接或通过总线连接。通过总线连接时,所有编码器的数据会以连续帧的形式同步到主设备,而不是单独传输。BiSS还实现了循环冗余校验(CRC)错误检测——这是一种比多次传输更可靠的方法。此外,BiSS还提供安全接口,适用于符合IEC 61508标准SIL3级别的安全应用。
Unlike SSI encoders, BiSS encoders can be connected point-to-point or via bus. When connected via bus, the data from all the encoders is clocked (synchronized) to the master in one continuous frame rather than individually. BiSS also implements a cyclic redundancy check (CRC) for error checking — a more reliable method than multiple transmission. There also exists a BiSS Safety interface, for safety applications up to SIL3 per IEC 61508.
Hiperface DSL
Hiperface DSL

Hiperface DSL,即高性能数字伺服链路接口,最初是SICK公司开发的专有接口。然而,在2016年,SICK公司开放了该接口,采用授权许可模式,允许其他制造商将这项技术集成到他们的产品中。
与之前的Hiperface不同,Hiperface DSL是一种全数字协议,仅使用两根线即可实现双向通信和编码器供电,这两根线与电机电源线捆绑在一起(尽管需要一个变压器来提高共模噪声抑制能力)。这使得电机和控制器无需单独的编码器连接。Hiperface DSL符合RS-485标准,数据传输速率为9.375 Mbaud。数据可以循环传输(尽可能快),也可以与控制器时钟同步传输。
Hiperface DSL, the HIgh PERformance InterFACE Digital Servo Link, was originally a proprietary interface developed by SICK. However, in 2016, SICK “opened up” the interface with a licensing model that allows other manufacturers to integrate the technology into their product offering.
Unlike its predecessor, Hiperface, Hiperface DSL is an all-digital protocol that uses just two wires for bi-directional communication and encoder power, bundled with the motor power cable (although a transformer is required to improve the common mode noise rejection). This gives the advantage of eliminating the need for separate encoder connections on the motor and the controller. Hiperface DSL complies with the RS-485 standard and and has a data transmission rate of 9.375 Mbaud. Data can be transmitted cyclically (as fast as possible) or synchronously with the controller clock.
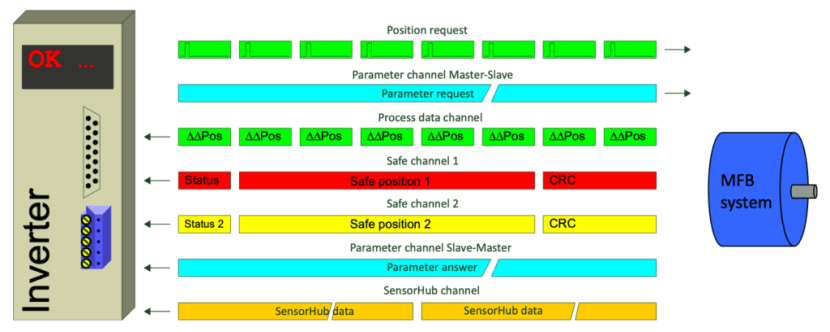
Hiperface DSL包含位置反馈、参数交换、过程数据、安全位置和状态监测(SensorHub)数据的通道,所有数据均通过两根可集成到电机电缆中的导线传输。
图片来源:Sick
Hiperface DSL includes channels for position feedback, parameter exchange, process data, safe position, and condition monitoring (SensorHub) data, all transmitted on two wires which can be integrated into the motor cable.
Image credit: Sick
Hiperface DSL架构还包含用于传输电机参数数据、状态监测数据和集成安全运动的通道,数据通过两条数字通信线路传输。这种冗余和错误检查机制使Hiperface DSL接口符合SIL3安全标准。
The Hiperface DSL architecture also includes channels for the transfer of motor parameter data, condition monitoring data, and integrated safe motion, with data being transmitted over two digital communication wires. This redundancy and error-checking make the Hiperface DSL interface compliant with SIL3 safety standards.
EnDat 2.2
EnDat 2.2

Heidenhain的编码器数据接口(EnDat 2.2)是一种同步双向标准,使用四根线进行通信——两根线分别用于差分数据和差分时钟信号——另外两根线用于供电,两根线用于电池缓冲或并联供电。EnDat 2.2 可提供高达 2 MHz 的时钟频率,在某些型号上,通过额外的传播延迟补偿,频率最高可达 16 MHz。
由于 Hiperface DSL 已成为“开放”接口,EnDat 现在是唯一仍然专有的绝对式编码器串行接口(但需要注意的是,原始的 Hiperface 协议也仍然是专有的)。
The Encoder Data, or EnDat 2.2, interface from Heidenhain is a synchronous, bidirectional standard that uses four wires for communication — two wires each for differential data and differential clock signals — plus two wires for power and two for either battery buffering or parallel power supply. EnDat 2.2 can provide clock frequencies of up to 2 MHz, and on some models, additional compensation for propagation delay makes frequencies up to 16 MHz possible.
Since Hiperface DSL has become an “open” interface, EnDat is now the only serial interface for absolute encoders that remains proprietary (although it should be noted that the original Hiperface protocol also remains proprietary).
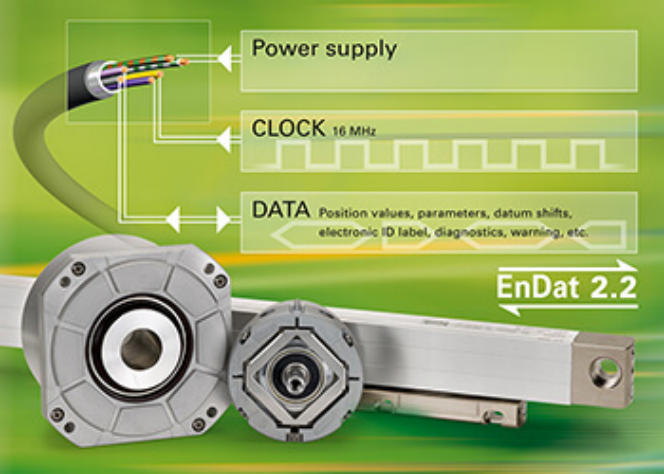
通过传播延迟补偿,EnDat 2.2 可提供高达 16 MHz 的时钟频率。
图片来源:Heidenhain
With propagation delay compensation, EnDat 2.2 can supply clock frequencies up to 16 MHz.
Image credit: Heidenhain
EnDat 2.2 还可以读取、写入或更新编码器中存储的信息,并将传感器信息或诊断信息等数据从编码器传输到控制器。传输的数据类型(例如绝对位置、诊断信息或参数信息)通过控制器向编码器发送模式命令。与 BiSS 和 Hiperface DSL 一样,EnDat 2.2 也符合 SIL3 安全标准。
EnDat 2.2. can also read, write, or update information stored in the encoder and can transfer data such as sensor information or diagnostic information from the encoder to the controller. The type of data transmitted — for example, absolute position, diagnostics, or parameter information — is sent via mode commands from the controller to the encoder. Like BiSS and Hiperface DSL, EnDat 2.2. is also compliant with SIL3 safety standards.
IO-Link
IO-Link
IO-Link 是一种用于连接传感器、执行器和自动化系统的工业通信协议。它由 IO-Link 社区开发,并作为国际标准 (IEC 61131-9) 进行管理。IO-Link 支持双向通信,可传输过程数据和设备参数。
IO-Link 采用点对点连接,可集成到各种网络拓扑结构中。它支持使用标准工业电缆进行简单的布线,并提供诊断功能以及自动设备参数化选项。
IO-Link is an industrial communication protocol for connecting sensors and actuators with automation systems. It was developed by the IO-Link community and is managed as an international standard (IEC 61131-9). IO-Link enables bidirectional communication and transmits both process data and device parameters.
IO-Link uses a point-to-point connection and can be integrated into various network topologies. It supports simple cabling via standard industrial cables and offers diagnostic functions as well as the option of automatic device parameterization.
EtherNet/IP
EtherNet/IP

EtherNet/IP™ 是一种广泛应用的以太网通信网络,它为用户提供在工业自动化应用中部署标准以太网技术(IEEE 802.3 与 TCP/IP 协议族相结合)的工具。EtherNet/IP 和 CIP 技术由全球贸易和标准制定组织 ODVA, Inc. 管理。
EtherNet/IP 提供多种网络拓扑选项,包括使用标准以太网基础设施设备的星型或线性拓扑,以及使用专门启用 EtherNet/IP 的设备级环网 (DLR)。符合 IEEE 以太网标准使用户能够选择不同的网络接口速度(例如 10 Mbps、100 Mbps 和 1 Gbps),并拥有灵活的网络架构,可兼容各种商用以太网安装选项,包括铜缆、光纤、光纤环网和无线网络。
EtherNet/IP™ 在会话层及以上实现 CIP,并在传输层及以下将 CIP 适配到特定的 EtherNet/IP™ 技术。EtherNet/IP 在物理层和数据链路层使用标准的 IEEE 802.3 技术。 EtherNet/IP 可以支持无限数量的点对点节点。在网络层和传输层,EtherNet/IP 使用标准的 TCP/IP(传输控制协议/互联网协议)在一个或多个设备之间发送消息。对于实时数据传输,EtherNet/IP 还采用基于 IP 的 UDP 协议来传输包含时间关键型控制数据的 I/O 消息。
EtherNet/IP™ is a widely adopted Ethernet communication network that provides users with the tools to deploy standard Ethernet technology (IEEE 802.3 combined with the TCP/IP Suite) in industrial automation applications. The EtherNet/IP and CIP technologies are managed by ODVA, Inc., a global trade and standards development organization.
EtherNet/IP offers various network topology options including star or linear with standard Ethernet infrastructure devices, or device level ring (DLR) with specially enabled EtherNet/IP devices. Compliance with IEEE Ethernet standards provides users with a choice of network interface speeds – e.g., 10, 100 Mbps and 1 Gbps – and a flexible network architecture compatible with commercially available Ethernet installation options including copper, fiber, fiber ring, and wireless.
EtherNet/IP™ implements CIP at the Session layer and above and adapts CIP to the specific EtherNet/IP™ technology at the Transport layer and below. EtherNet/IP uses standard IEEE 802.3 technology at the Physical and Data Link layers. EtherNet/IP can accommodate an unlimited number of point-to-point nodes. At the Network and Transport layers, EtherNet/IP utilizes standard TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol) to send messages between one or more devices. For real-time data transfer, EtherNet/IP also employs UDP over IP to transport I/O messages that contain time-critical control data.
EtherCAT
EtherCAT

EtherCAT® 最初由 Beckhoff 开发,旨在实现 MAC 数据包的即时处理,并为自动化应用提供实时以太网连接。它能够为整个自动化系统提供可扩展的连接,从大型 PLC 一直延伸到 I/O 和传感器层。
EtherCAT® 是一种针对过程数据优化的协议,使用标准的 IEEE 802.3 以太网帧。每个从节点在帧传输过程中处理其数据报并将新数据插入帧中。该过程在硬件(MAC 层)中完成,因此每个节点的处理延迟极低,从而实现最快的响应时间。
EtherCAT® 是一种 MAC 层协议,对任何更高层的以太网协议(例如 TCP/IP、UDP、Web 服务器等)都是透明的。它可以在一个系统中连接多达 65,535 个节点。EtherCAT® 主站可以是标准的以太网控制器,从而简化网络配置。由于每个从节点的延迟都很低,EtherCAT® 可提供灵活、低成本且网络兼容的工业以太网解决方案。
EtherCAT® was originally developed by Beckhoff to enable on-the-fly MAC packet processing and deliver real-time Ethernet to automation applications. It can provide scalable connectivity for entire automation systems, from large PLCs all the way down to the I/O and sensor level.
EtherCAT® is a protocol optimized for process data, using standard IEEE 802.3 Ethernet Frames. Each slave node processes its datagram and inserts the new data into the frame while each frame is passing through. The process is handled in hardware (at the MAC layer) so each node introduces minimum processing latency, enabling the fastest possible response time.
EtherCAT® is a MAC layer protocol and is transparent to any higher level Ethernet protocols, such as TCP/IP, UDP, Web server, etc. It can connect up to 65,535 nodes in a system. The EtherCAT® master can be a standard Ethernet controller, thus simplifying the network configuration. Due to the low latency of each slave node, EtherCAT® delivers flexible, low-cost and network-compatible industrial Ethernet solutions.
PROFIBUS
PROFIBUS

PROFIBUS 是 PROFIBUS & PROFINET International (PI) 制定的基于现场总线的自动化标准。PROFIBUS 通过单根总线电缆,将控制器或控制系统与现场的分布式设备(传感器和执行器)连接起来,并支持与更高层级的通信系统进行一致的数据交换。PROFIBUS 的一致性得益于其采用的单一、标准化的、与应用无关的通信协议(称为 PROFIBUS DP)。该协议在工厂和过程自动化、运动控制以及安全相关任务中均能支持现场总线解决方案。
PROFIBUS is the fieldbus-based automation standard of PROFIBUS & PROFINET International (PI). Via a single bus cable, PROFIBUS links controller or control systems with decentralized field devices (sensors and actuators) on the field level and also enables consistent data exchange with higher ranking communication systems. Consistency of PROFIBUS is enabled by utilizing a single, standardized, application-independent communication protocol (named PROFIBUS DP), which, without any difference, supports fieldbus solutions both in factory and process automation as well as in motion control and safety-related tasks.
PROFINET
PROFINET

PROFINET® 被西门子和通用电气等主要工业设备制造商广泛采用。它分为三个不同的等级:
• PROFINET A 级通过代理访问 PROFIBUS 网络,利用 TCP/IP 远程过程调用桥接以太网和 PROFIBUS。其周期时间约为 100 ms,主要用于参数数据和循环 I/O。典型应用包括基础设施和楼宇自动化。
• PROFINET B 级,也称为 PROFINET 实时 (PROFINET RT),引入了基于软件的实时方法,并将周期时间缩短至约 10 ms。B 级通常用于工厂自动化和过程自动化。
• PROFINET C 级 (PROFINET IRT) 是同步实时的,需要专用硬件将周期时间缩短至 1 ms以下,以便在实时工业以太网上为运动控制操作提供足够的性能。
PROFINET RT 可用于 PLC 类应用,而 PROFINET IRT 则非常适合运动控制应用。分支型和星型是PROFINET常用的拓扑结构。PROFINET网络需要精心规划拓扑结构才能达到系统所需的性能。
PROFINET® is widely used by major industrial equipment manufacturers such as Siemens and GE. It has three different classes:
• PROFINET Class A provides access to a PROFIBUS network through proxy, bridging Ethernet and PROFIBUS with a remote procedure calling on TCP/IP. Its cycle time is approximately 100 ms, and is primarily used for parameter data and cyclic I/O. The typical application includes infrastructure and building automation.
• PROFINET Class B, also referred as PROFINET Real-Time (PROFINET RT), introduces a softwarebased real-time approach and has reduced the cycle time to approximately 10 ms. Class B is typically used in factory automation and process automation.
• PROFINET Class C (PROFINET IRT), is Isochronous and real-time, requiring special hardware to reduce the cycle time to less than 1ms to deliver sufficient performance on the real-time industrial Ethernet for motion control operations.
PROFINET RT can be used in PLC-type applications, while PROFINET IRT is a good fit for motion applications. Branch and Star are the common topology used for PROFINET. Careful topology planning is required for PROFINET networks to achieve the required performance of the system.
CANopen
CANopen

控制区域网络 (CAN) 总线是一种高完整性串行总线系统,最初是作为汽车总线开发的,后来被用作工业自动化现场总线之一。CANopen® 是一种基于 CAN 的通信系统。它包含更高层的协议和规范,并提供物理层和数据链路层,用于实现高达 1 Mbps 的串行通信。CANopen® 和 DeviceNet™ 是基于 CAN 总线标准化的更高层协议,旨在实现同一工业网络中设备的互操作性。CANopen® 支持网络上 127 个节点,而 DeviceNet™ 支持同一网络上 64 个节点。
EPC CANopen® 编码器使用通信规范 CiA 301 和设备规范 CiA 406 V3.2 C2 类。
Control Area Network (CAN) bus, is a high-integrity serial bus system originally created as an automotive vehicle bus, which later came to be used as one of the fieldbuses for industrial automation. CANopen® is a CAN-based communication system. It comprises higher-layer protocols and profile specifications and provides a physical and data link layer for serial communication with speeds up to 1 Mbps. CANopen® and DeviceNet™ are higher level protocols standardized on top of CAN bus to allow interoperability with devices on the same industrial network. CANopen® supports 127 nodes on the network while DeviceNet™ supports 64 nodes on the same network.
EPC CANopen® encoders use communication profile CiA 301 and device profile CiA 406 V3.2 class C2.
SAE J1939
SAE J1939

SAE J1939 是由美国汽车工程师协会 (SAE) 制定的一套标准,主要用于卡车、巴士、工程机械等重型车辆以及其他商用车辆的通信和诊断。
J1939 定义了电子控制单元 (ECU) 如何通过控制器局域网 (CAN) 总线协议传输数据,从而实现车辆部件之间的通信和诊断。
它为设备间的交互创建了一种通用的共享“语言”,使得重型车辆可以安装来自不同制造商的设备,而无需担心兼容性问题。
SAE J1939, a set of standards defined by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), is primarily used for communication and diagnostics in heavy-duty vehicles like trucks, buses, and construction equipment, as well as other commercial vehicles.
J1939 defines how Electronic Control Units (ECUs) transmit data over the Controller Area Network (CAN) bus protocol, enabling communication and diagnostics between vehicle components.
It creates a universal shared "language" for devices to interact, allowing heavy-duty vehicles to be fitted with devices from different manufacturers without worrying about incompatibility.
声明:
-文章转载自EPC, MOTION CONTROL TIPS,由爱泽工业翻译,如有侵权,请联系删除!
-如有偏颇,欢迎指正!

 沪公网安备31011002006738号
沪公网安备31011002006738号

