从人工到智能:机器人焊接重塑工业焊接新生态(中英文)
什么是机器人焊接?它是一种利用机器人焊接以极高的精度和速度连接金属的技术。到2025年,工厂将广泛采用机器人焊接,利用先进的机械臂将生产效率提升到超越人类的能力水平。与手工焊接相比,这种自动化可以将生产效率提高高达50%。机器人焊接起源于20世纪60年代,如今已发展得非常成熟,配备机械臂的机器人在制造过程中发挥着至关重要的作用。
What is robotic welding? It is a technology that uses robots welding to join metals with exceptional accuracy and speed. In 2025, factories widely employ robotic welding, utilizing advanced Robotic Arms to enhance production efficiency beyond human capabilities. This automation can boost productivity by up to 50% compared to manual welding. Originating in the 1960s, robotic welding has evolved significantly, with robots equipped with Robotic Arms now playing a crucial role in manufacturing processes.
时间段 | 增长和重要性 |
1960s | 机器人开始在美国工厂中使用 |
1980s | 汽车公司开始广泛使用机器人焊接 |
2005 | 北美有超过12万台机器人;其中约一半用于焊接 |
目前 | 机器人焊接约占所有工业机器人工作的20%。 |
Time Period | Evidence of Growth and Significance |
1960s | Robots started being used in U.S. factories |
1980s | Car companies began using robotic welding extensively |
2005 | Over 120,000 robots worked in North America; about half performed welding |
Present | Robotic welding accounts for about 20% of all industrial robot jobs |
要点总结
Key Takeaways
• 机器人焊接利用机器人快速,精准地连接金属。这有助于提高工厂效率,保障工人安全。焊接机器人包含机械臂,传感器和控制器等重要部件。这些部件确保每次都能实现牢固均匀的焊接。人工智能和协作机器人等新技术使机器人焊接更加智能、安全。这些变革正在塑造未来工厂的运作方式。
• Robotic welding uses robots to join metals fast and accurately. This helps factories work better and keeps workers safer. Welding robots have important parts like robot arms, sensors, and controllers. These parts help make strong and even welds every time. New technology like AI and cobots make robotic welding smarter and safer. These changes are shaping how factories will work in the future.
什么是机器人焊接?
What Is Robotic Welding?

定义与目的
Definition and Purpose
什么是机器人焊接?这是一个当今非常重要的问题。机器人焊接是指利用机器人自主完成焊接工作。这些机器人能够以极高的速度和精度连接金属部件。其主要目标是通过让机器人重复执行相同的工作,从而提高产品产量并实现更高质量的焊接。工厂使用焊接机器人来完成大型焊接作业,以便让焊工能够专注于难度更高或更特殊的项目。
机器人焊接始于20世纪60年代。最初的系统虽然简陋,但却改变了工厂的运作方式。多年来,机器人焊接技术不断进步,日臻完善。如今,焊接机器人利用传感器和智能控制系统来实现牢固均匀的焊接。使用机器人进行焊接有助于避免疲劳工人操作失误,并保障人员免受高温和烟雾的危害。
What is robotic welding? This is an important question today. Robotic welding uses robots to do welding jobs by themselves. These robots join metal pieces with great speed and accuracy. The main goal is to make more products and better welds by letting robots do the same job over and over. Factories use welding robots for big jobs, so human welders can work on harder or special projects.
Robotic welding began in the 1960s. The first systems were basic, but they changed how factories worked. Over the years, robot welding got better and smarter. Now, welding robots use sensors and smart controls to make strong and even welds. Using robots for welding helps stop mistakes from tired workers and keeps people safe from heat and fumes.
工作原理
How It Works
机器人焊接工艺使用可编程的机械臂。机械臂沿着预先设定的路径移动焊枪。工程师或程序员告诉机器人该做什么。首先,团队规划焊接步骤并对机器人进行编程。然后,机器人会反复执行这些步骤,精度极高。
传感器帮助机器人找到合适的焊接位置。摄像头和激光器检测金属部件的位置。机械臂稳定地握住焊枪,并以合适的速度移动。电源为焊枪提供能量,熔化金属并形成牢固的焊缝。机器人可以向三个方向移动,到达人类无法到达的地方。
现代焊接机器人采用新技术。一些机器人利用人工智能在工作过程中调整焊接方式。即使金属本身并非完美无瑕,也能确保焊缝牢固。工厂使用机器人焊接进行多种类型的焊接,例如电弧焊,点焊和激光焊。
The robot welding process uses a robot arm that can be programmed. The robot arm moves a welding torch along a planned path. Engineers or programmers tell the robot what to do. First, the team plans the welding steps and programs the robot. The robot then does these steps again and again with high accuracy.
Sensors help the robot find the right place to weld. Cameras and lasers check where the metal parts are. The robot arm holds the torch steady and moves it at the right speed. The power supply gives energy to the torch, which melts the metal and makes a strong weld. The robot can move in three directions and reach places people cannot.
Modern welding robots use new technology. Some robots use artificial intelligence to change how they weld while working. This keeps the welds strong, even if the metal is not perfect. Factories use robot welding for many types of welding, like arc, spot, and laser welding.
主要部件
Main Components
焊接机器人由许多重要部件组成。每个部件都对机器人系统的正常运行起着至关重要的作用。下表列出了主要部件及其功能:
Welding robots have many important parts. Each part helps the robot system work well. Here is a table that lists the main parts and what they do:
组件 | 功能 |
机械臂 | 将焊枪移动到正确的位置和角度 |
焊枪 | 加热并连接金属部件 |
送丝机 | 以合适的速度输送焊丝 |
电源 | 提供焊接所需的能量 |
控制器 | 向机器人发送指令 |
示教器 | 用于编程和控制的手持设备 |
传感器 | 确定零件位置并检查焊接质量 |
夹具和工作台 | 焊接时用于固定金属部件 |
安全系统 | 通过防护罩和紧急停止装置保障工人安全 |
Component | Function |
Robot Arm | Moves the welding torch to the right spot and angle |
Welding Torch | Heats up and joins the metal pieces |
Wire Feeder | Feeds welding wire at the right speed |
Power Supply | Gives the energy needed for welding |
Controller | Sends instructions to the robot |
Teach Pendant | Handheld device for programming and control |
Sensors | Find part position and check weld quality |
Fixtures & Table | Hold the metal parts steady while welding |
Safety Systems | Keep workers safe with shields and emergency stops |
焊接机器人还会使用一些辅助工具,例如焊丝清洁器和指示灯。焊丝清洁器可以清除焊枪上的飞溅物,从而延长工具的使用寿命。指示灯则用于显示焊接单元是否正在运行或需要帮助。
Welding robots also use extra tools like wire cleaners and stack lights. Wire cleaners take off spatter from the torch, which helps the tools last longer. Stack lights show if the welding cell is working or needs help.
机器人焊接的特点和类型
Robotic Welding Features and Types
主要特点
Key Features
机器人焊接为当今工厂提供了诸多实用功能。其中一项显著优势是精度。焊接机器人利用专用传感器跟踪焊缝并控制焊接过程。这些传感器帮助机械臂每次都能将焊枪精准定位。部分传感器还能让机器人感知工作区域并实时调整焊接参数。控制系统则负责管理焊接速度,焊枪角度和送丝速度,从而确保每次焊接都牢固均匀。工厂需要定期维护和培训机器人,以确保其高效运行。
Robot welding has many helpful features for factories today. One big benefit is precision. Welding robots use special sensors to follow seams and control welding. These sensors help the robot arm put the torch in the right place every time. Some sensors let robots see the work area and make changes as they go. Control systems help manage speed, torch angle, and wire feed. This makes sure each weld is strong and even. Factories need to do regular maintenance and training to keep robots working well.
机器人焊接类型
Robot Welding Types
工厂在许多工作中会使用不同类型的机器人焊接设备。主要类型有:
MIG 焊接:使用焊丝和保护气体。适合快速完成大批量焊接作业。
氩弧焊:使用钨电极进行焊接,焊缝干净,精确。
点焊:将金属薄片在小点处连接起来。常见于汽车制造厂。
电弧焊:利用电弧熔化并连接金属。
激光焊接:利用激光束进行精细,复杂的焊接。
等离子焊接:利用等离子弧进行深而牢固的焊接。
Factories use different robot welding types for many jobs. The main types are:
MIG welding: Uses a wire electrode and shielding gas. It is good for fast, big jobs.
TIG welding: Uses a tungsten electrode for clean, precise welds.
Spot welding: Joins metal sheets at small points. It is common in car factories.
Arc welding: Uses an electric arc to melt and join metals.
Laser welding: Uses a laser beam for fine, detailed welds.
Plasma welding: Uses a plasma arc for deep, strong welds.
焊接类型 | 最佳应用场景 | 主要特性 |
MIG 焊 | 高速,大批量焊接 | 快速,可重复 |
氩弧焊 | 薄金属焊接,光洁度高 | 精度高 |
点焊 | 钣金,汽车 | 快速,牢固的连接 |
电弧焊 | 通用制造 | 用途广泛,坚固耐用 |
激光焊接 | 电子产品,医疗部件 | 精细加工,低热量 |
等离子焊接 | 适用于厚金属,重型工件 | 穿透深度深 |
Welding Type | Best Use Case | Key Feature |
MIG | High-speed, large batches | Fast, repeatable |
TIG | Thin metals, clean finish | High precision |
Spot | Sheet metal, automotive | Quick, strong joints |
Arc | General fabrication | Versatile, robust |
Laser | Electronics, medical parts | Fine detail, low heat |
Plasma | Thick metals, heavy duty | Deep penetration |
安全与效率
Safety and Efficiency
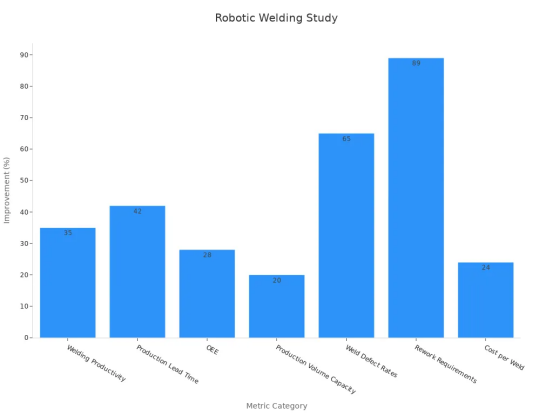
机器人焊接使工厂更安全、更高效。机器人承担危险作业,使工人能够远离高温和火花。机器人内置传感器可以检测障碍物并在必要时停止工作,从而有效预防事故。机器人焊接还能帮助节约材料和能源,提高生产速度,减少浪费。研究表明,机器人焊接可将生产率提高 35%,并将交货周期缩短 42%。
Robot welding makes factories safer and more efficient. Robots do dangerous jobs, so workers stay away from heat and sparks. Sensors in robots can find obstacles and stop the work if needed. This helps prevent accidents. Robot welders also help save materials and energy. This makes production faster and less wasteful. Studies show robot welding can boost productivity by 35% and cut lead times by 42%.
应用及未来趋势
Applications and Future Trends
行业应用
Industry Applications
机器人焊接如今在许多领域都至关重要。在汽车工厂,机器人承担了大部分焊接工作。它们在车身和装配线上作业,帮助打造更坚固、更安全的汽车,并加快生产速度。电子和医疗器械工厂也使用机器人进行精细的焊接作业。在能源和交通领域,像 TYCROP 这样的公司使用人工智能机器人。这些机器人可以处理各种不同的零件,并在人手不足时提供帮助。下表展示了机器人焊接在不同地区和不同行业中的应用情况:
Robot welding is now very important in many fields. In car factories, robots do most of the welding jobs. They work on car bodies and in assembly lines. These robots help make cars strong and safe. They also help build cars faster. Electronics and medical factories use robots for tiny, careful welds. In energy and transport, companies like TYCROP use robots with AI. These robots handle many different parts and help when there are not enough workers. The table below shows how robot welding is growing in different places and jobs:
方面 | 细节 |
汽车行业增长 | 2023 年为 22.6 亿美元,2032 年为 57 亿美元 |
制造业增长 | 5.4 亿美元(2023 年)至 13.4 亿美元(2032 年) |
关键区域 | 北美,欧洲,亚太地区 |
关键驱动因素 | 自动化,质量,劳动力短缺 |
Aspect | Details |
Automotive Growth | $2.26B (2023) to $5.7B (2032) |
Manufacturing Growth | $0.54B (2023) to $1.34B (2032) |
Regional Leaders | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific |
Key Drivers | Automation, quality, labor shortages |
2025 年创新展望
Innovations for 2025
机器人焊接技术正在快速发展。协作机器人 (Cobot) 现在可以安全地与人并肩工作。这些协作机器人利用传感器和摄像头来预防事故。企业可以使用即插即用的便捷机器人,也可以选择以服务形式租赁机器人。新型机器人利用人工智能 (AI) 在工作过程中自动调整焊接设置,从而提高焊接质量。增强现实 (AR) 和虚拟现实 (VR) 技术有助于在安全的数字化环境中培训工人。一些公司正在尝试使用意念控制机器人,但这仍处于起步阶段。专家认为,到 2025 年,将会有更多的数字化工具,绿色机器和智能检测技术涌现。
• 协作机器人帮助工厂完成更多工作,填补就业空缺。
• 人工智能和云工具帮助机器人变得更加智能。
• 简易的编程方式让任何人都能教会机器人焊接。
Robot welding is changing quickly. Cobots can now work safely next to people. These cobots use sensors and cameras to stop accidents. Companies use easy plug-and-play robots and rent robots as a service. New robots use AI to change welding settings while working. This makes welds better. Augmented reality and virtual reality help train workers in safe, digital worlds. Some companies are trying mind-controlled robots, but this is still new. Experts think there will be more digital tools, green machines, and smart checks by 2025.
• Cobots help factories do more work and fill job gaps.
• AI and cloud tools help robots get smarter.
• Easy programming lets anyone teach a robot to weld.
声明:
-文章转载自EVST,由爱泽工业翻译,如有侵权,请联系删除!
-如有偏颇,欢迎指正!

 沪公网安备31011002006738号
沪公网安备31011002006738号

