机械臂组件:各部件的工作原理及应用领域
机械臂的组成部分包括底座和安装系统、关节和连杆、执行器以及末端执行器(夹爪或工具)。
这些相互连接的部件协同工作,控制着机械臂的运动、精度以及承重能力,无论是大型六轴工业机器人还是小型桌面型机器人,都离不开它们。
了解每个部件的功能有助于选择合适的机械臂、进行升级或维护其平稳运行。良好的配置能够提高精度、延长使用寿命,并满足各种应用需求,无论是工厂作业、医疗应用还是科研项目。
Robotic arm components include the base and mounting system, joints and links, actuators, and the end effector (gripper or tool).
These interconnected parts work together to control movement, accuracy, and how much weight the arms can handle in both large six-axis industrial robots and small desktop models.
Knowing what each part does makes it easier to pick the right arm, upgrade it, or keep it running smoothly. A good setup improves accuracy, lasts longer, and matches the needs of the job, whether it’s factory work, medical use, or research projects.
什么是机械臂组件?
What are robotic arm components?
机械臂组件是指使机械臂能够移动、感知和操作物体的部件。底座、关节、执行器、传感器和末端执行器在自动化任务中各自发挥着不同的作用。
例如,一个高效的系统依赖于选择合适的机械臂底座,这会影响机器人在表面或平台上运行的稳定性。
了解关节类型和执行器系统可以帮助工程师根据实际应用(例如取放或机床上下料)来调整机械臂的性能。
这些组件也构成了更专业化机械臂的基础,从机械臂到气动臂,甚至是专为工厂应用设计的紧凑型机械臂。
Robotic arm components are the parts that let the arm move, sense, and manipulate objects. The base, joints, actuators, sensors, and end effector each have a distinct role in automation tasks.
For example, an effective system relies on choosing the right robot arm base, which affects how securely the robot can operate on a surface or platform.
Understanding joint types and actuator systems can help engineers match the arm’s performance to real-world applications like pick-and-place or machine tending.
These components also form the foundation for more specialized builds, from mechanical arms to pneumatic variants, or even compact models designed for factory use.
机械臂的核心部件
Core parts of a robotic arm
机械臂的核心部件(例如末端执行器)协同工作,产生可控且可重复的运动,模拟人臂的肩部、肘部和腕部运动。
• 底座和安装系统:底座将机械臂固定在平面、工作台或移动平台上。稳定的机械臂底座对于精度和负载支撑至关重要,尤其是在工业环境中。
• 关节和连杆:关节为机械臂提供自由度,而连杆连接各个节段。大多数机械臂包含三个关节部分:肩部、肘部和腕部。这些关节决定了机械臂的活动范围和灵活性。它们是机械臂的关键部件,影响着机械臂在空间中的运动方式。
• 执行器:每个关节处的电机或气缸控制运动。执行器将控制信号转化为物理运动,使机械臂能够精确定位。
• 末端执行器(夹爪或工具):这是机械臂与物体交互的部分。根据应用的不同,末端执行器可以是机械夹爪、焊枪、螺丝刀或吸盘。它相当于“手”,是机器人手最重要的组件之一。
模块化系统还允许根据任务需求更换或升级这些机器人手臂部件。
The core components of a robotic arm (e.g., the end effector) work together to create controlled, repeatable motion that mimics the shoulder, elbow, and wrist of a human arm.
• Base and mounting system: The base anchors the arm to a surface, workbench, or mobile platform. A stable robot arm base is essential for precision and load support, especially in industrial environments.
• Joints and links: Joints provide degrees of freedom for the arm, while links connect each segment. Most robot arms include three jointed sections: shoulder, elbow, and wrist. These define the robot’s reach and flexibility. These are critical components of a robotic arm that influence how it can move in space.
• Actuators: Motors or pneumatic cylinders at each joint control the motion. Actuators translate control signals into physical movement, allowing the robot to position its arm with accuracy.
• End effector (gripper or tool): This is the part of the arm that interacts with objects. Depending on the application, the end effector might be a mechanical gripper, welding torch, screwdriver, or suction cup. It functions as the “hand,” making it one of the most important robot hand components.
Modular systems also allow these robot arm parts to be swapped or upgraded based on task requirements.
执行器、电机和运动控制
Actuators, motors, and movement control
执行器通过将能量转化为机械力来控制机械臂的运动。它们决定了关节的精度、速度和重复性。
最常见的执行器类型包括:
• 旋转电机,例如伺服电机或步进电机,可驱动旋转关节,并能精确控制速度和角度。
• 线性执行器沿直线伸缩,从而移动机械臂的某个部分。
• 气动或液压驱动装置,利用压缩空气或流体压力提供快速、强劲的运动,常用于高速装配或抓取任务。
每个执行器都接收来自控制器的信号,并将其转化为特定关节的运动。这种控制器到电机的回路协调多轴运动。
选择合适的执行器取决于所需的有效载荷、精度和运行环境。用于搬运小型零件的轻型机械臂可以使用紧凑型电机,而重型任务通常需要更强大的液压或气动系统。
Actuators control robotic arm movement by converting energy into mechanical force. They determine precision, speed, and repeatability across joints.
The most common actuator types include:
• Rotary electric motors, such as servo or stepper motors, power rotational joints with high control over speed and angle.
• Linear actuators extend or retract in a straight line to move a part of the arm.
• Pneumatic or hydraulic drives, which use compressed air or fluid pressure to deliver fast, strong motions, are often used in high-speed assembly or gripping tasks.
Each actuator receives signals from the controller, translating them into motion at specific joints. This controller to motor loop coordinates multi axis motion.
Selecting the right actuator depends on your required payload, precision, and operating environment. Lightweight arms for small parts handling may use compact electric motors, while heavy-duty tasks often demand more powerful hydraulic or pneumatic systems.
夹爪机构和末端执行器类型
Gripper mechanisms and end effector types
末端执行器是机械臂的“手”,夹爪是最常见的类型。它根据任务需要抓取、固定或操作物体。
机械手组件有多种类型,每种都适用于不同的环境:
• 机械夹爪使用爪子或手指夹持物体。它们广泛用于取放、包装和机器装载。
• 真空吸盘夹爪适用于平坦或光滑的表面,例如盒子或玻璃面板,尤其适用于物流和仓储系统。
• 磁性夹爪非常适合在制造或数控加工中处理铁磁性金属零件。
• 由柔性材料制成的软体夹爪可以适应不规则形状,因此在食品加工或处理易碎物品时非常有用。
机械臂附件的类型决定了机械臂操作物体的安全性和效率。
例如,在电子制造中,精密夹爪可以最大限度地减少对易碎元件的损坏。相比之下,重型仓库系统可能更注重速度和可靠性,而非精细控制。
在许多现代系统中,末端执行器采用模块化设计,允许单个机械臂在不同工具间切换,从而实现更高的灵活性。这种适应性使其成为各行各业不可或缺的工具,无论是在制造业、实验室工作,甚至是纺织品处理(例如缝纫机器人)等领域,都离不开机器人手臂的应用。
The end effector is the robotic arm’s “hand,” and the gripper is its most common type. It grips, holds, or manipulates items depending on the task.
There are several types of robotic hand components, each suited for different environments:
• Mechanical grippers use jaws or fingers to clamp onto objects. These are widely used for pick-and-place, packaging, and machine loading.
• Vacuum suction grippers work well with flat or smooth surfaces, such as boxes or glass panels, especially in logistics and warehouse systems.
• Magnetic grippers are ideal for handling ferrous metal parts in manufacturing or CNC operations.
• Soft grippers made from flexible materials can conform to irregular shapes, making them useful in food processing or when handling delicate items.
The type of robotic arm attachment determines how safely and effectively the arm can manipulate objects.
In electronics manufacturing, for instance, precision grippers minimize damage to fragile components. In contrast, a heavy-duty warehouse system may prioritize speed and reliability over fine control.
End effectors are modular in many modern systems, allowing one arm to switch between tools for greater versatility. This adaptability makes them essential across industries using robot arms for manufacturing, lab work, or even textile handling, like sewing robots.
传感器和反馈系统
Sensors and feedback systems
机械臂中的传感器提供位置,力和环境的实时数据。这些反馈使系统能够调整运动,从而确保精度和安全性。
如果没有传感器,机械臂将盲目运行,无法纠正错位、碰撞或任务中的各种变化。
最常见的机械臂传感器类型包括:
• 编码器,用于跟踪关节位置和旋转角度,以保持机械臂的精确运动。
• 力和扭矩传感器,通常位于腕部或末端执行器附近,用于检测抛光、装配或零件插入等任务中的压力或阻力。
• 视觉系统,使用摄像头,有时还会结合人工智能,来检测物体的位置、形状、方向和缺陷。
这些传感器与控制软件协同工作,实现动态反馈回路。例如,如果零件略微偏离位置,机器人可以检测到偏移并调整其轨迹,这对于质量检测或电子组装等高精度工作至关重要。
先进的机械臂传感器还能提升协作环境中的安全性。例如,Standard Bots 的 RO1 系统利用集成视觉和碰撞检测功能,无需围栏即可在人员周围安全运行。
添加传感器可以将机械臂转变为响应灵敏的系统,因此在评估现代应用中机械臂部件和功能时,传感器升级至关重要。
Sensors in a robotic arm provide real-time data on position, force, and environment. This feedback lets the system adjust movements for accuracy and safety.
Without sensors, robotic arms would operate blindly, unable to correct for misalignment, collisions, or variability in tasks.
The most common types of robot arm sensors include:
• Encoders, which track joint positions and rotational angles to maintain precise arm movements.
• Force and torque sensors, usually placed near the wrist or end effector, are used to detect pressure or resistance during tasks like polishing, assembly, or part insertion.
• Vision systems, using cameras and sometimes AI, to detect object position, shape, orientation, and defects.
These sensors work together with the control software to enable dynamic feedback loops. If a part is slightly out of place, for example, the robot can detect the offset and adjust its trajectory, which is critical for high-precision work like quality inspection or electronics assembly.
Advanced robotic arm sensors also improve safety in collaborative settings. Systems like Standard Bots’ RO1 use integrated vision and collision detection to operate safely around people without fencing.
Adding sensors transforms a mechanical arm into a responsive system, making it one of the most important upgrades when evaluating robotic arm parts and function for modern applications.
材料与结构设计
Materials and structural design
机械臂结构采用的材料需兼顾强度、重量和耐久性,以满足性能需求。材料的选择直接影响机械臂的移动速度、举升能力以及在反复受力下的使用寿命。
常见的机械臂材料包括:
• 铝因其轻质、耐腐蚀和成本效益而备受青睐。它广泛应用于中端机械臂的制造和研发领域。
• 碳纤维具有极高的强度重量比。碳纤维机械臂能够以更低的能量消耗实现更快的移动速度,使其成为精密任务或移动机器人的理想选择。
• 钢材用于重型工业机械臂,在这些应用中,高有效载荷和刚性比重量更为重要。钢材虽然耐用,但由于其质量较大,会限制移动速度。
机械臂的机械框架通常由管材、板材和外壳组合而成。它必须支撑执行器和线路,同时还要能够抵抗振动和变形。良好的机械臂结构能够确保在高速或高负载运行过程中保持稳定。
轻量化设计有助于提高机械臂的灵活性并降低能耗,尤其是在安装在移动平台或天花板龙门架上的机械臂中。例如,碳纤维机械臂可以降低取放系统的惯性并缩短循环时间。
材料的选择始终与应用场景密切相关。洁净室机械臂优先考虑表面光滑且不易脱落的材料,而室外机械臂则需要耐候涂层。了解这些权衡取舍对于为应用选择合适的机械臂组件至关重要。
Robotic arm structures use materials that balance strength, weight, and durability to meet performance demands. The choice of material directly impacts how fast the arm can move, how much it can lift, and how long it lasts under repeated stress.
Common robotic arm materials include:
• Aluminum is valued for its light weight, corrosion resistance, and cost-effectiveness. It’s widely used in mid-range arms for manufacturing and research.
• Carbon fiber, which offers high strength-to-weight ratios. Arms made from carbon fiber can move faster with less energy, making them ideal for precision tasks or mobile robots.
• Steel is used in heavy-duty industrial arms where high payload and rigidity are more important than weight. It’s durable but limits speed due to its mass.
The arm’s mechanical frame is often a combination of tubes, plates, and housings. It must support actuators and wiring while resisting vibration and deformation. A good robotic arm structure ensures stability during high-speed or high-load operations.
Lightweight designs also help with more agile movement and lower energy consumption, especially in robotic arms mounted on mobile platforms or ceiling gantries. For example, carbon fiber robot arms reduce inertia and cycle time in pick-and-place systems.
Material selection is always tied to use cases. Cleanroom arms prioritize smooth surfaces and non-shedding materials, whereas outdoor arms need weatherproof coatings. Understanding these trade-offs is key when reviewing a robotic arm components list for your application.
专用机械臂类型
Specialized robotic arm types
专用机械臂专为特定环境而设计,例如重工业、康复或娱乐场所。这些机械臂通常采用定制组件或材料以满足独特的性能需求,展现了机械臂设计的多样性和灵活性。
• 工业机械臂注重速度、精度和耐用性。其组件的设计旨在应对长时间生产周期中的焊接、装配和数控加工。例如 RO1 机械臂的有效载荷为 18 公斤,臂展为 1300 毫米,在工业机械臂部件类别中优于典型的紧凑型机械臂。
• 人体机械臂专注于假肢和康复。这些轻型机械臂使用软致动器和肌电传感器来辅助运动或恢复活动能力,并通过肌肉信号或脑机接口提供直接控制。
• 机械动画手臂应用于电影、主题公园和研究领域。这些手臂注重逼真的动作和表情,而非工业性能,并强调流畅的运动、静音运行和外观的真实性。
• 电子手臂或仿生手臂处于机器人学和神经科学的前沿领域。这些手臂通常处于实验阶段,它们与人类神经系统或人工智能驱动的预测模型深度集成,以模拟或扩展自然运动。
Specialized robotic arms are designed for targeted environments, such as heavy industry, rehabilitation, or entertainment. These arms often use custom components or materials to match unique performance needs, and they demonstrate how diverse and flexible robotic arm design has become.
• Industrial robotic arms are built for speed, precision, and endurance. Their components are designed to handle welding, assembly, and CNC tending over long production cycles. Arms like RO1 include an 18 kg payload and 1300 mm reach, outperforming typical compact arms in the industrial robotic arm parts category.
• Robotic arms for humans focus on prosthetics and rehabilitation. These lightweight arms use soft actuators and EMG sensors to assist with movement or restore mobility, offering direct control via muscle signals or brain-computer interfaces.
• Animatronic arms are used in film, theme parks, and research. These focus on lifelike motion and expression rather than industrial performance, with attention to fluid motion, quiet operation, and cosmetic realism.
• Electronic or cyborg arms exist at the frontier of robotics and neuroscience. Often experimental, these arms integrate deeply with the human nervous system or AI-driven prediction models to simulate or extend natural movement.
2025年机器人手臂的应用
Applications of robotic arms in 2025
到2025年,凡是需要高精度,一致性或重复性动作的场合,机器人手臂都将至关重要。它们在工厂,医院,教室和娱乐工作室等场所都将十分常见。
In 2025, robotic arms will be essential wherever precision, consistency, or repetitive motion is required. They are common in factories, hospitals, classrooms, and entertainment studios.
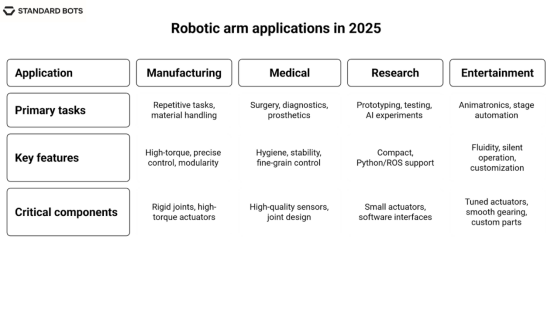
表格展示了 2025 年机器人手臂在制造业,医疗,科研和娱乐等领域的应用。
Table showing robotic arm applications in 2025 across manufacturing, medical, research, and entertainment.
1. 制造和工业自动化
在制造业中,机械臂执行重复性高、产量大的任务,例如焊接、物料搬运、零件组装、打磨和检测。这些系统依靠刚性结构关节、高扭矩执行器和精确控制来处理高达 18 公斤的有效载荷。
像 RO1 这样的模块化机械臂设计灵活,操作人员可以快速切换工具,用于数控加工、螺丝拧紧、抛光或激光应用。这种适应性最大限度地减少了设置时间,并提高了高混合生产环境中的正常运行时间。
2. 医疗和辅助技术
机械臂可辅助外科手术、诊断、假肢和物理治疗。在外科手术机器人领域,机械臂可提供毫米级的精度,用于微创手术。为残障人士设计的辅助机械臂则依靠轻质材料、流畅的关节运动和来自生物传感器的灵敏反馈。
在此,机械臂组件必须优先考虑卫生、稳定性和精细控制,因此传感器质量和关节设计对成功至关重要。
3. 研究与教育
机械臂广泛应用于实验室原型制作、重复测试和人工智能实验。学校也利用它们教授学生力学、编程和控制理论。
此类机械臂大多结构紧凑,采用小型执行器,并支持 Python 或 ROS 操作系统。研究人员利用它们开发机器视觉模型、测试人机交互 (HRI) 或在受控条件下评估实际性能。
4. 娱乐与创意工作
机械动画手臂可为电影道具、主题公园和舞台自动化提供逼真的动作。这些手臂优先考虑流畅性和静音运行,采用精密调校的执行器和顺滑的齿轮传动装置。
设计人员通常会定制机械臂部件,尤其是关节和夹爪,以模仿人类或动物的逼真动作。
1. Manufacturing and industrial automation
In manufacturing, robotic arms perform repetitive, high-volume tasks such as welding, material handling, part assembly, sanding, and inspection. These systems rely on rigid structural joints, high-torque actuators, and precise control to handle payloads up to 18 kg.
Modular arms like RO1 are designed for flexibility, allowing operators to quickly switch between tools for CNC tending, screwdriving, polishing, or laser applications. This adaptability minimizes setup time and boosts uptime in high-mix production environments.
2. Medical and assistive technology
Robotic arms assist in surgeries, diagnostics, prosthetics, and physical therapy. In surgical robotics, arms offer millimeter-level accuracy for minimally invasive procedures. Assistive arms for disabled users rely on lightweight materials, smooth joint movement, and responsive feedback from biosensors.
Here, the arm components must prioritize hygiene, stability, and fine-grain control, making sensor quality and joint design critical to success.
3. Research and education
Robotic arms are widely used in labs for prototyping, repetitive testing, and AI experiments. Schools use them to teach students about mechanics, programming, and control theory.
Most arms in this category are compact, use small actuators, and support Python or ROS. Researchers use them to develop machine vision models, test HRI (human-robot interaction), or benchmark real-world performance under controlled conditions.
4. Entertainment and creative work
Animatronic arms deliver realistic motion for movie props, theme parks, and stage automation. These arms prioritize fluidity and silent operation, using finely tuned actuators and smooth gearing.
Designers often customize the robot arm parts, especially the joints and grippers, to mimic human or animal ges tures with lifelike motion.
选择合适的机械臂组件
Choosing the right robotic arm components
选择合适的机械臂组件取决于任务有效载荷、精度、工作空间和集成需求。每个部件的选择都必须符合性能目标、安全标准和可用预算。
Choosing the right robotic arm components depends on your task’s payload, precision, workspace, and integration needs. Each part must be selected to match performance goals, safety standards, and available budget.
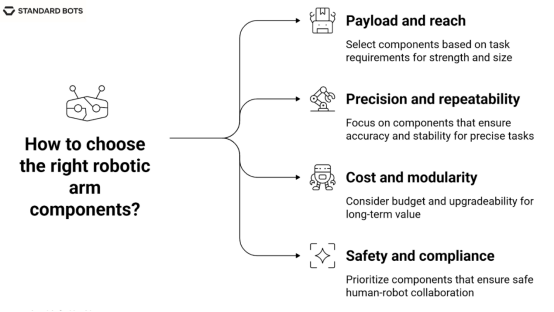
图示为选择机械臂组件的四个因素:有效载荷和臂展、精度和重复性、成本和模块化、安全性和合规性。
Diagram showing four factors for choosing robotic arm components: payload and reach, precision and repeatability, cost and modularity, safety and compliance.
• 首先考虑有效载荷和工作范围。像数控机床上下料或码垛这样的高负载任务需要更坚固的关节、更重的底座和高扭矩执行器。而像零件检测或 3D 打印这样的轻型作业则需要更小的电机和更紧凑的占地面积。
• 在电子、质量保证或外科手术辅助等应用中,精度和重复性至关重要。编码器、扭矩传感器和精细的运动控制在这些应用中发挥着关键作用。此外,还需要刚性结构组件来最大限度地减少振动或漂移。
• 成本和模块化设计会影响长期价值。RO1 提供工业级规格的产品,价格低于 4 万美元,无需完全重新设计即可支持多种应用场景。模块化设计允许升级特定的机械臂部件,例如更换夹爪或传感器,而无需更换整个系统。
• 安全性和合规性对于协作工作至关重要。如果附近有人员操作,请选择支持碰撞检测、力限制关节和机器视觉的组件。为了选择合适的机械臂部件,请检查该系统是否支持与常用工具或软件平台的即插即用集成。
• Start with payload and reach. High-load tasks like CNC machine tending or palletizing need stronger joints, heavier bases, and high-torque actuators. Lightweight jobs like part inspection or 3D printing require smaller motors and a compact footprint.
• Precision and repeatability matter in applications like electronics, QA, or surgical assistance. Here, encoders, torque sensors, and fine-grain motion control become critical. You’ll also need rigid structural components to minimize vibration or drift.
• Cost and modularity influence long-term value. RO1 offers industrial-grade specs for under $40K, supporting multiple use cases without full redesign. Modular designs let you upgrade specific arm parts, like swapping out grippers or sensors, without replacing the whole system.
• Safety and compliance must be factored in for collaborative work. If humans operate nearby, choose components that support collision detection, force-limited joints, and machine vision. For assistance in selecting the right robotic arm parts, check whether the system supports plug-and-play integration with common tools or software platforms.
总结
Summing up
机械臂是由五个关键部件组成的精密机器,这些部件决定了机械臂的性能。底座提供稳定性,关节实现灵活运动,执行器提供精确的运动控制。传感器提供实时反馈,用于精度和安全监控。
成功与否取决于部件与特定应用的匹配,无论是装配、焊接还是机床上下料。末端执行器(例如夹爪和吸盘)使机械臂能够适应不同的任务,而铝、碳纤维和钢等材料的选择则会影响其耐用性和速度。
精明的制造商会选择模块化设计,以便于升级,从而最大限度地提高正常运行时间和投资回报率。在当今竞争激烈的市场环境中,合适的机械臂配置对于运营效率至关重要。
Robotic arms are sophisticated machines built from five key components that determine their performance. The base provides stability, joints enable flexible movement, and actuators deliver precise motion control. Sensors offer real-time feedback for accuracy and safety monitoring.
Success depends on matching components to specific applications, whether assembly, welding, or machine tending. End effectors like grippers and suction cups adapt arms to different tasks, while material choices between aluminum, carbon fiber, and steel affect durability and speed.
Smart manufacturers choose modular designs that allow easy upgrades, maximizing uptime and return on investment. In today's competitive landscape, the right robotic arm configuration can make or break operational efficiency.
常见问题解答
FAQs
1. 机械臂的主要组成部分有哪些?
机械臂的主要组成部分包括底座、关节、连杆、执行器、传感器、控制器和末端执行器。每个部件都有其独特的作用:底座固定机械臂,关节决定其运动,执行器产生力,末端执行器执行实际任务。
这些机械臂部件及其功能共同作用,使其能够在工业,医疗和科研应用中实现协调、可重复的运动。
1. What are the main components of a robotic arm?
The main components of a robotic arm include the base, joints, links, actuators, sensors, controller, and end effector. Each part has a distinct role: the base anchors the arm, joints define its motion, actuators generate force, and the end effector performs the actual task.
Together, these robotic arm parts and functions allow for coordinated, repeatable movement across industrial, medical, and research applications.
2. 机械臂上的哪个部件充当“手”?
末端执行器充当机械臂的“手”,安装在机械臂的末端,用于与物体交互。它可以是夹爪、吸盘、工具头或用于装配或检测等任务的专用爪。
根据作业的不同,可以选择或更换机械臂的部件,以满足力需求、物体形状或速度要求。
2. What component acts as the “hand” on a robot arm?
The end effector acts as the robot’s “hand,” mounted at the end of the arm to interact with objects. It can take the form of a gripper, suction device, toolhead, or specialized jaw for tasks like assembly or inspection.
Depending on the job, you can choose or replace robot hand components to match force requirements, object shape, or speed.
3. 机械臂可以使用哪些类型的夹爪?
机械臂可使用的夹爪类型包括机械爪、气动吸盘、磁性夹爪和软体自适应夹爪。机械夹爪非常适合精确操作,而软体夹爪则用于处理不规则或易碎物品。
经常会在包装、电子和纺织等行业看到专用的机械臂附件。
3. What types of grippers can a robotic arm use?
The types of grippers a robotic arm can use include mechanical claws, pneumatic suction cups, magnetic pickers, and soft adaptive grippers. Mechanical grippers are ideal for precise handling, while soft grippers handle irregular or fragile items.
You’ll often find specialized robotic arm attachments used in industries like packaging, electronics, and textiles.
4. 执行器如何驱动机械臂运动?
执行器通过将能量转化为运动来驱动机械臂运动,使机械臂能够旋转、伸展或收缩。电动机(伺服电机或步进电机)驱动旋转关节;线性执行器使部件沿直线运动;气动或液压系统则增加速度或动力
执行器的类型会影响机械臂每个组件在执行任务时的精度和力度。
4. How do actuators power robotic arm movement?
Actuators power robotic arm movement by converting energy into motion, allowing robotic arms to rotate, extend, or contract. Electric motors (servo or stepper) drive rotary joints; linear actuators move parts in straight lines; and pneumatic or hydraulic systems add speed or power.
The type of actuator affects how accurately and forcefully each robot arm component performs during a task.
5. 哪些传感器有助于控制机械臂?
有助于控制机械臂的传感器包括编码器、力传感器和扭矩传感器以及视觉系统。编码器跟踪关节位置,力传感器检测阻力,视觉系统用于对齐物体。这些传感器协同工作,提供实时反馈,这对电子组装或手术机器人等高精度任务至关重要。
5. What sensors help control a robotic arm?
The sensors that help control a robotic arm include encoders, force and torque sensors, and vision systems. Encoders track joint positions, force sensors detect resistance, and vision systems align objects. Together, these sensors provide real-time feedback critical for high-precision tasks like electronics assembly or surgical robotics.
6. 机械臂通常由哪些材料制成?
机械臂通常由铝制成,以保证轻便灵活;由碳纤维制成,以实现高速精准;或由钢制成,以保证强度和耐用性。材料的选择会影响负载能力、能耗和使用寿命。
高性能碳纤维机械臂在狭小空间或动态环境中需要快速灵活移动时尤为有用。
6. What materials are robotic arms typically made from?
Robotic arms are typically made of aluminum for lightweight versatility, carbon fiber for high-speed precision, or steel for strength and durability. The choice of material impacts load capacity, energy consumption, and lifespan.
High-performance carbon fiber robot arms are especially useful when fast, agile movement is required in tight spaces or dynamic environments.
声明:
-文章转载自STANDARD BOTS,由爱泽工业翻译,如有侵权,请联系删除!
-如有偏颇,欢迎指正!

 沪公网安备31011002006738号
沪公网安备31011002006738号

