HUNGER密封塑料材质介绍(中英文)
塑料根据其物理性能可分为四类:
Plastics can be divided into four groups according to their physical properties:
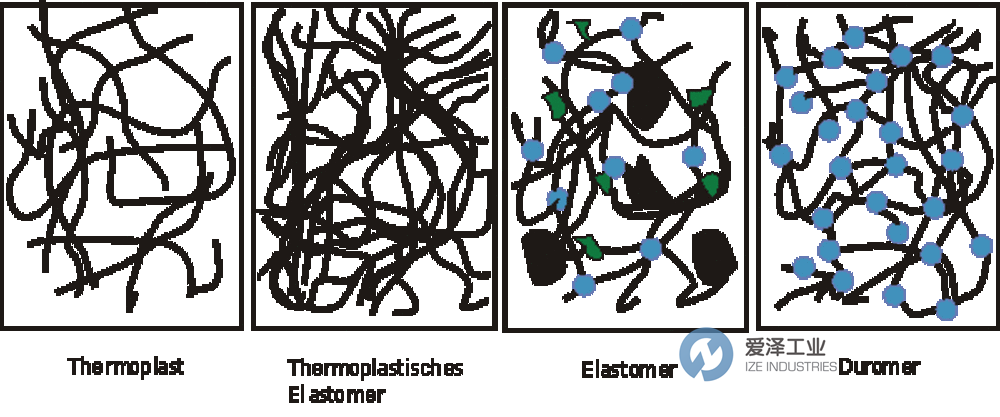
热塑性塑料
Thermoplastics
热塑性塑料是软质、粘塑性或硬质的塑料。它们通过加热而熔化,然后具有延展性。这是由于它们的内部组成是未交联的直链或支链分子。目前工业生产的聚合物的大部分(约占总产量的 80%)属于这一类。
Thermoplastics are plastics which can be soft, viscoplastic or hard. They are melted by heating and are then malleable. This is due to their internal composition of unbranched or branched chain molecules which are uncrosslinked. The far bigger part of the nowadays industrially manufactured Polymers (approx. 80 % of the total production) belongs to this group.
弹性体
Elastomers
弹性体是轻微交联的,通常具有较长的链并且在环境温度下具有弹性。根据应用温度和玻璃化转变温度之间的关系,它们可以是硬质到硬弹性或软弹性。它们的基本特征之一是在熔化前分解。弹性体与热塑性塑料的区别在于大分子的交联。与热固性材料相比,弹性体含有相对较长、未交联且缠结的分子部分
Elastomere are slightly cross-linked, are often of comparatively long chains and have elastic properties at ambient temperature. Depending on the relation between application temperature and glass transition temperature they are hard upto hard-elastic or soft-flexible. It is one of their basic characteristics that they decompose before they melt. Elastomers distinguish themselves from the thermoplastics by the cross-linking of macromolecules. In contrast to thermosets elastomers contain comparatively long, uncrosslinked and entangled molecular moieties
热塑性弹性体
Thermoplastic Elastomers
热塑性弹性体结合了环境温度下硫化弹性体(橡胶)的机械性能和热塑性塑料的加工性能。
Thermoplastic Elastomers combine the mechanical properties of vulcanized elastomers (rubber) at ambient temperature and the processability of thermoplastics.
硬质聚合物
Duromers
硬质聚合物在加热时会变硬,并且不会再次变软。硬化是通过聚合物分子的空间集中、主要是共价交联来实现的。目前,硬质聚合物在数量上不如热塑性塑料重要。
Duromers harden when heated up and do not become soft again. The hardening is achieved by spatially focused, mostly covalente cross-linking of Polymer molecules. Duromers are currently quantitatively less important than thermoplastics.
声明:
- 文章转载自HUNGER DFE,由爱泽工业翻译,如有侵权,请联系删除!
- 如有偏颇,欢迎指正!

 沪公网安备31011002006738号
沪公网安备31011002006738号

